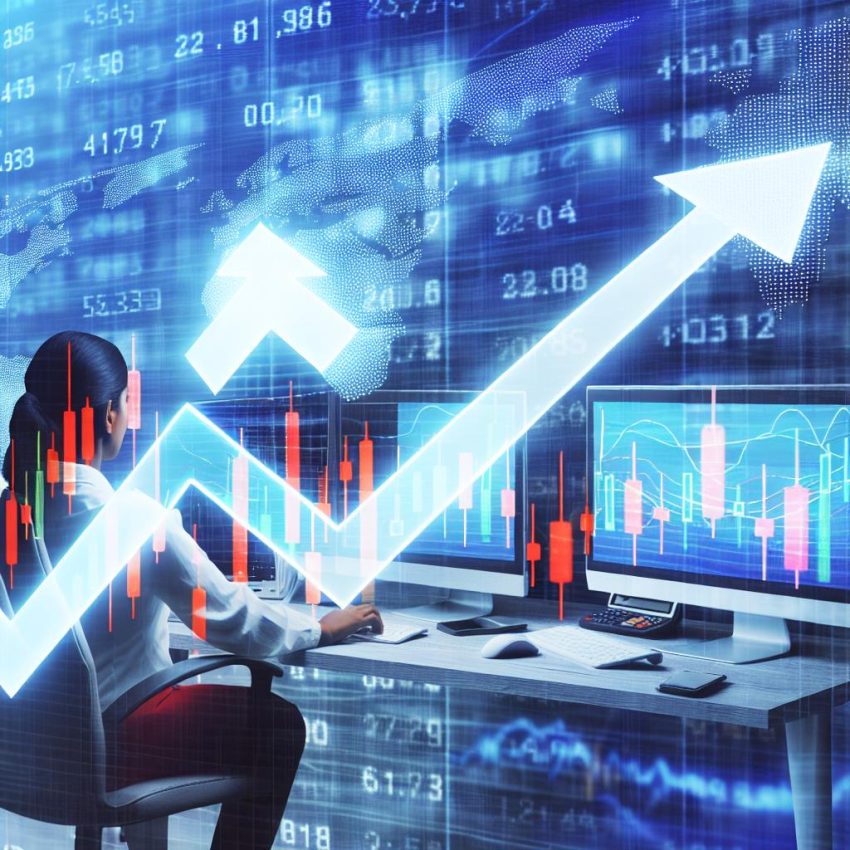
Understanding Scalping Trading
Scalping trading is a method that involves executing numerous trades throughout the trading day to capitalize on small price movements. This style of trading is fast-paced and requires traders to make quick decisions, often within seconds or minutes. The primary objective of scalping is to achieve small but consistent profits that can accumulate over time. While it may not suit every trader’s style, it appeals to those who thrive in high-energy environments and have a good understanding of market dynamics.
The Basics of Scalping
Scalping generally involves holding positions for a very short time frame, often just seconds to minutes, rarely more than an hour. Traders using this strategy aim to catch small moves in price by exploiting the bid-ask spread or benefiting from minor price fluctuations. They rely on technical analysis, using real-time charts and data to make informed decisions. A high-speed internet connection and access to an efficient trading platform are essential for scalping.
To engage in scalping, traders need to be highly disciplined, as the rapid nature of the trading requires split-second decision-making. Unlike other trading strategies that may focus on long-term trends or gross profit margins, scalping aims at accumulating incremental gains. This requires identifying and executing favorable trades rapidly, demanding acute attention to detail and vigilance over market movements.
Common Scalping Techniques
Scalpers employ various techniques to gain an edge in the market. These methodologies are formulated to exploit different market conditions and price dynamics to the trader’s advantage. Below are some common scalping techniques employed by many traders:
Market Making: This technique involves placing both buy and sell orders around the current market price. In doing so, traders profit from the bid-ask spread, which, although minor per trade, can accumulate to significant returns due to the high volume of trades. A market maker provides liquidity to the market by being ready to buy and sell, making them a critical part of the trading ecosystem.
Order Flow Analysis: This technique involves understanding the flow of market orders, volume patterns, and the overall liquidity in the market. By analyzing the details of buy and sell orders, scalpers gain insights into the demand and supply pressure, enabling them to execute trades accordingly. This method requires sophisticated tools and a deep understanding of market microstructures.
Range Trading: For this technique, scalpers identify a security’s price range, then buy at the low end and sell at the high end. Range trading requires an accurate assessment of support and resistance levels within a predetermined timeframe. Scalpers must be adept at analyzing price charts to identify and exploit these price ranges effectively.
Risk Management in Scalping
Given the high frequency of trades and rapid market movement in scalping, effective risk management is pivotal. Scalpers need robust risk control strategies to prevent potential losses. Due to the small profit margins typical in scalping, one or several losing trades can quickly erode profits, making risk management an integral component of the strategy.
Position Sizing: Scalpers typically trade with only a small portion of their capital per trade, thereby minimizing potential losses. Position sizing ensures that no single trade holds the power to significantly affect the trader’s overall capital.
Stop Loss Orders: These are predetermined exit points that help limit potential losses on each trade. By setting a stop loss, a trader ensures that the trade is automatically exited if the market moves unfavorably past a certain threshold, thereby protecting their capital.
Risk-Reward Ratios: Scalpers assess the potential profit against potential loss before executing a trade to ensure favorable outcomes. This involves calculating the expected profit compared to the potential loss, with a ratio that typically favors higher potential profit.
Tools and Resources for Scalpers
Deploying a scalping strategy requires the right tools and resources. These are instrumental in providing the speed, data, and insights necessary to make the quick decisions that scalping demands.
Trading Platforms: Traders need access to brokerage platforms that offer fast execution and real-time data. The choice of platform can significantly impact a trader’s efficiency and effectiveness in implementing their scalping strategy.
Charting Software: High-quality charting software pertains to the real-time analysis necessary for identifying trade opportunities. The software enables traders to analyze charts with precision, utilizing multiple technical indicators and tools.
News Feeds: Access to real-time news is crucial for making informed trading decisions. As market trends and prices can be influenced by news events, staying updated with the latest developments can provide a competitive edge.
In conclusion, scalping trading offers an opportunity for quick profits, but it requires swift decision-making, advanced technical analysis skills, and stringent risk management strategies. While it can be highly rewarding, it is essential for traders to thoroughly understand the dynamics of the market and use the appropriate tools and techniques for successful scalping.
Scalping as a trading strategy necessitates a strong mental framework and exceptional execution skills. Scalpers must cultivate patience, perseverance, and precision to master this high-stakes trading approach. As markets become increasingly complex and competitive, continued learning and adaptation are crucial to stay ahead in the world of scalping trading. With meticulous preparation and a comprehensive understanding of market intricacies, scalpers can navigate the challenges of this dynamic trading style and potentially achieve substantial cumulative profits.
This article was last updated on: March 23, 2025